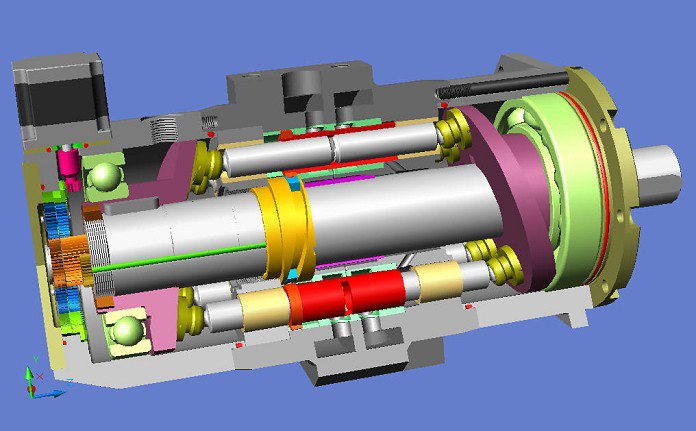
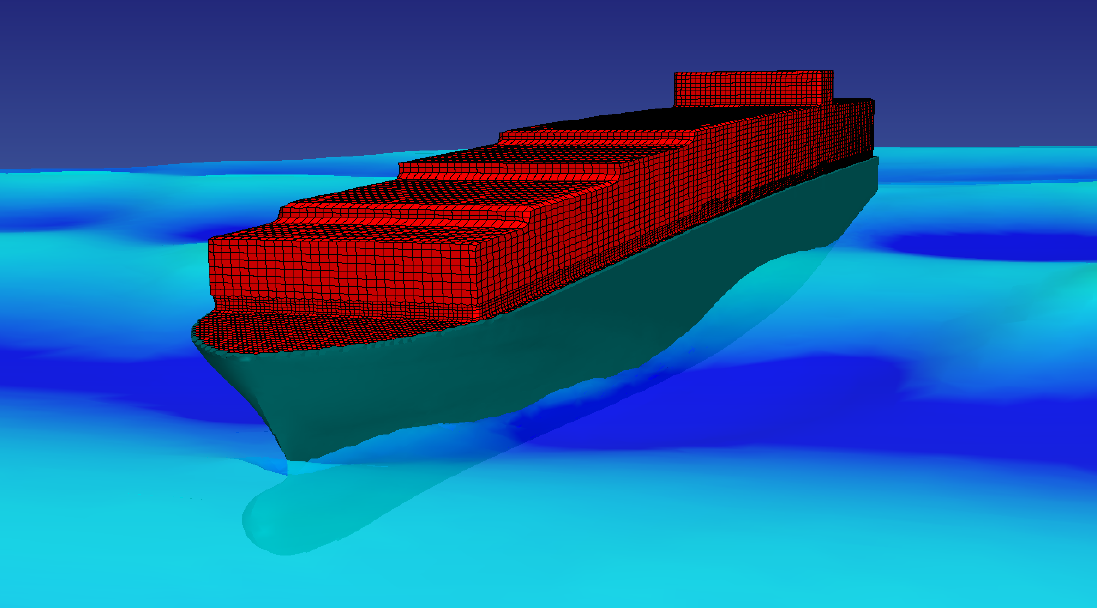
When a surrounding fluid exerts pressure on a flexible structure, this structure deforms, which leads to changes in the flow field of the fluid. These so-called fluid-structure interactions appear in different application areas: the most common examples are wings, spoilers and other deformable parts of racing or everyday cars or the flutter of aircraft wings. Furthermore, this effect can be observed in many machines, especially where moving parts or light, very deformable walls are involved. Typical examples are valves, pumps or hydraulic engine mounts. MpCCI has been used successfully to solve different applications from all of these areas:
Flexible Structures in Aerodynamics and Machinery Design
Tabbed contents
Reference Applications
Why FSI is so Important to Win the next Race in Formula1
With Formula 1 being one of the most popular motorsports on the globe, there is always high pressure to provide excellent performance as a way to retain existing and attract new audiences. As the FIA regulations are quite clear-cut in terms of limitations leading to a close competition, engineers are digging for the smallest advantages. This leads to taking interactions of CFD with other physical effects into account to get a complete understanding of all effects involved. MpCCI CouplingEnvironment from Fraunhofer SCAI has been integrated into the design workflows of leading F1 teams and is successfully used to optimize the aerodynamic behavior of the car while taking the structural behavior into account.

Recent Progress in Flow Control for Practical Flows
This book explores the outcomes on flow control research activities carried out within the framework of two EU-funded projects focused on training-through-research of Marie Sklodowska-Curie doctoral students. The main goal of the projects described in this monograph is to assess the potential of the passive- and active-flow control methods for reduction of fuel consumption by a helicopter. The research scope encompasses the fields of structural dynamics, fluid flow dynamics, and actuators with control. Research featured in this volume demonstrates an experimental and numerical approach with a strong emphasis on the verification and validation of numerical models. The book is ideal for engineers, students, and researchers interested in the multidisciplinary field of flow control.
Chapter 15 "Analysis and Optimization of Flow Around FlexibleWings and Blades Using the Standard Co-simulation Interface MpCCI" will give some valuable examples on how MpCCI has been used to calculate and optimise different wing configurations.
Aero-Elastic Benchmark Cases using Coupled Fluid-Structure Code Combinations
Using MpCCI to couple MSC.Nastran and Ansys Fluent, different benchmarks from the area of aero-elasticity, most importantly the HIRENASD benchmark, have been simulated. The results of the coupled FSI simulations are compared to experimental measurements.
Numerical Simulation of Fluid-Structure Interaction in the Design Process for a New Axial Hydraulic Pump
With the help of numerical simulation, a new high-pressure hydraulic axial pump has been developed at Gdansk University. To find an optimal layout of the different pump chambers, coupled FSI simulations, using Abaqus, Fluent and MpCCI, were used.
An Enhanced 1-Way Coupling Method to Predict Elastic Global Girder Loads
To predict global hull girder loads of sea-going vessels, the structural elasticity has to be taken into account. A one-way-mapping of the CFD external loads at the hull surface to a FEA 3D model of the hull computing the structural response has been realized by employing MpCCI.
MpCCI Methods
FSI Features in MpCCI
- Different coupling schemes are available:
- A globally explicit coupling method: The coupled fields are exchanged only once per coupling step. This approach is applicable to problems with weak physics coupling.
- An implicit iterative coupling method: The coupled fields are exchanged several times per coupling step until an overall stabilized solution is achieved before advancing to the next coupling step. This approach is applicable to problems with strong physics coupling.
- Each coupling scheme can be adapted to the application:
- Optimization of the implicit iterative coupling with an adaptive stopping criteria
- Explicit coupling method with flexible time coupling management
- Application with highly coupled time: time steps are matching, or one code is acting as master code and defining the time step size
- Application with different solver integration on time scale: non matching time steps
- Analysis of a stationary application by coupling two steady state simulations
- Quasi-transient approach by coupling a steady state and transient simulations
- Ramping and relaxation methods to stabilize coupled simulations. The relaxation factor can be computed automatically according to Aitken’s method.
- Extrapolation methods can be used to handle “orphaned areas” (local mesh regions without matching regions on the partner mesh)
- Additional to the CFD code’s morphing and remeshing capabilities, the MpCCI Mesh Morpher can be used to handle the deformation of the CFD mesh, e.g. for coupled OpenFOAM simulations.
- MpCCI FSIMapper can be used to check the geometries and the mapped CFD results before starting a coupled simulation.
Realization of new Methods and Solutions within R&D Projects
- Although FSI is already an established solution method for many engineering applications, there are still many open issues which we would like to evaluate and solve in more strategic and long-term (3rd party funded) R&D projects:
- Extending MpCCI to further simulation tools and deploying it to new and challenging application domains
- Working on open and generic benchmarks and validation cases
- Enhancing stability and accuracy for highly dynamic fluid-structure interactions
- More sophisticated and automated coupling control mechanisms
Software and Services
Our FSI Service Offer
Based on our long-term experience in FSI, we can provide you with dedicated knowledge and services:
- Integration of commercial or inhouse codes into the MpCCI tools
- Integration of MpCCI tools into customer’s CAE workflow
- Adjusting MpCCI to customer’s specific requirements
- Realization of a first FSI concept for your specific application setup – from separated standalone models towards coupled fluid-structure-cases
- Preparation of the geometrical connection between the CFD and FEA meshes
- Defining appropriate mesh motion conditions for the CFD simulation code
- Testing and evaluating different coupling methods for your specific problem: iterative or explicit coupling, steady state or transient simulations
- Integrating coupled FSI jobs in your dedicated HPC systems
MpCCI CouplingEnvironment
The MpCCI CouplingEnvironment offers flexible solutions for multiphysical simulations. The combinable simulation codes for this application area are shown in the following table:
Discipline |
Codes |
|---|---|
Fluid |
|
STRUCTURE |
|
The supported quantities in this context are:
Quantities |
|
|---|---|
Mechanical |
|
MpCCI FSIMapper
The MpCCI FSIMapper maps simulation results from a source to a target mesh. The following two tables list the supported source and target file formats for this application area.
Source Formats |
Quantities |
|
|---|---|---|
CFD |
|
pressure |
Target Formats |
Target Analyses |
|
|---|---|---|
FEM |
|
deformation stress fatigue NVH |
List of additionally supported source and target file formats